The Contribution of Host Cells to Pneumocystis Immunity

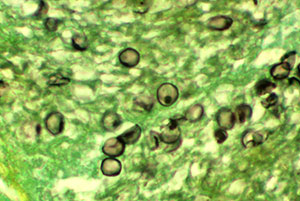
Pneumocystis is a pervasive fungus that is found world-wide. The genus of Pneumocystis has genetically heterogeneous species that have co-evolved so specifically with their mammalian hosts that they are obligate intra-pulmonary pathogens.
Pneumocystis jirovecii causes Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in immunocompromised humans. PCP can be life-threatening due to respiratory failure. The disease was first observed in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients but it is increasingly seen in immunocompromised non-AIDS patients.
New strategies for diagnosis and treatment of PCP are needed as it evolves epidemiologically and is so often life-threating. A profounder understanding of host immune responses to Pneumocystis jirovecii will improve the chances of developing new treatment strategies and therapies against PCP. Otieno-Odhiambo and Dr Hoving highlight recent studies in the field on the role of host immunity against Pneumocystis.
Read the paper - The Contribution of Host Cells to Pneumocystis Immunity: An Update
Article by Bonamy Holtak
